Number
Pattern and function
Data handling
Shape and Space
The students in
Early childhood
will:
Read, write and model numbers to 20
Count, compare and order numbers to 20
Estimate quantities to 10
Use ordinal numbers to describe the position of things in a sequence
Model number relationships to 10: “Show me one more than three,
take two cubes away from these cubes”
Use language of mathematics: more, less, number names, total
Use 1:1 correspondence
Explore the conservation of number through the use of manipulatives (xxxx
= x x x x)
Select and explain an appropriate method for solving a problem
Find and describe simple patterns
Create simple patterns using real objects
Sort and label real objects into sets by attributes
Create a graph of real objects and compare quantities using number words
Discuss and identify outcomes that will happen, won’t happen and
might happen

Identify, compare and describe attributes of real objects and situations: longer, shorter, heavier, empty, full, hotter, colder
Identify, compare and sequence events in their daily routine: before,
after, bedtime, storytime, today, tomorrow
Sort, describe and compare 3-D shapes according to attributes such as size or form
Explore and describe the paths, regions and boundaries of their immediate
environment (inside, outside, above, below) and their position (next
to, behind, in front of, up, down)
Number
Pattern and function
Data handling
Shape and Space
The students in
Year 1
will:
Begin to read, write and order all numbers from 0 to 100;
Understand and use the vocabulary of comparing and ordering these numbers
Count forwards and backwards from any small number, and in fives and tens from zero to one hundred
Estimate quantities to 50
Understand the operation of addition, and of subtraction (as 'take away'
or 'difference'), and use the related vocabulary and symbols
Begin to memorize simple number facts
Use fraction names (half and quarter) to describe part and whole relationships
Create, describe and extend patterns
Recognize, describe and extend patterns in numbers: odd and even, skip
counting by 5s and 10s
Identify simple patterns and rules for addition and subtraction
Solve simple problems by sorting, classifying and organizing information in various ways
Discuss, interpret and compare data represented in teacher generated
diagrams: tree, Carroll and Venn
Begin to understand the purpose of graphing data

Estimate, measure, label and compare using non-standard units of measurement: length, mass or capacity
Begin to understand why we use standard units of measurement to measure
Use a calendar to determine the date and to identify and begin to sequence
days of the week and months of the year
Tell time to the hour
Use everyday language to describe features of familiar 3-D and 2-D shapes
Sort and label 2D and 3D shapes using appropriate vocabulary: sides,
corners, circle, sphere, cube
Create 2D shapes
Number
Pattern and function
Data handling
Shape and Space
The students in
Year 2
will:
Count, read, write and order whole numbers to at least 100; know what each digit represents (including 0 as a place holder).
Read,
write and model numbers, using the base 10 system.
Read, write and model addition and subtraction to 20 (with and without
regrouping).
Understand that subtraction is the inverse of addition.
? Recall addition and subtraction facts to 10.
Use knowledge that addition can be done in any order to do mental calculations
more efficiently.
Understand the operation of multiplication as repeated addition or as
describing an array in real world contexts, using manipulatives, diagrams,
and symbols.
Use fraction names (half and quarter) to describe part and whole relationships.
Create,
describe and extend patterns.
Recognize, describe and extend patterns in numbers: odd and even, skip
counting, 2s, 5s and 10s, counting on, counting back.
Explore patterns in fact families.

Record,
organize, classify, display and understand data in a variety of simple
ways
Discuss, interpret and compare data represented in teacher generated
diagrams: tree, Carroll and Venn
Understand the purpose of graphing data
Create a pictograph and simple bar graph from a graph of real objects,
and interpret data by comparing quantities: more, fewer, less than,
greater than
Discuss, identify, predict and place outcomes in order of likelihood: impossible, unlikely, likely, certain

Estimate, measure and compare lengths, masses and capacities, using standard units
Understand
why we use standard units of measurement to measure
Use a calendar to determine the date and to identify and sequence days
of the week and months of the year
Read a simple scale to the nearest labelled division, including using
a ruler to draw and measure lines to the nearest centimetre
Estimate, identify and compare lengths of time, second, minute, hour,
day, week, month
Read and write the time to the hour, half hour and quarter hour
Use the mathematical names for common 2-D and 3-D shapes; sort shapes and describe some of their features
Find and explain symmetry in their immediate environment
Create and explain simple symmetrical patterns
Use mathematical vocabulary to describe position, direction and movement
Number
Pattern and function
Data handling
Shape and Space
The students in
Year 3
will:
Read, write and order numbers to 1000 and understand what each digit represents
Estimate quantities to at least 100
Count on or back in tens or hundreds from any two- or three-digit number
Count in 3s, 4s, 5s, and explore other numbers
Recognize unit fractions such as 1/2, 1/3, 1/4, 1/5, 1/10, and begin
to use them to find fractions of shapes and numbers
Add and subtract mentally a 'near multiple of 10' to or from a two-digit
number
Reasonably estimate answers to 100, using rounding and approximation
Know by heart all addition and subtraction facts for each number to
20
Know by heart facts for the 2, 3, 4, 5 and 10 multiplication tables
Choose and use appropriate operations to solve word problems, explaining methods and reasoning
Understand and be able to explain the relationship between the number
operations., addition and subtraction, multiplication and division
Identify patterns in number systems to 100

Discuss, compare and create sets from data that has subsets using tree, Carroll, Venn and other diagram
Design a survey, process and interpret the data
Solve a given problem by organizing and interpreting numerical data
in simple lists, tables and graphs
Collect and display data in a bar graph and interpret results
Use the scale on the vertical axis of a bar graph to represent large
quantities
Read and write the time to the minute using intervals of fifteen minutes, ten minutes and five minutes on a 12-hour clock
Estimate, measure, label and compare using formal methods and standard
units of measurement: length, mass, time and temperature
Select appropriate tools and units of measurement
Begin to understand and use monetary notation

Identify right angles
Identify lines of symmetry in simple shapes and recognize shapes with
no lines of symmetry
Number
Pattern and function
Data handling
Shape and Space
The students in
Year 4
will:
Read, write and model numbers, using the base 10 system, to 1000
Count, compare and order numbers to 1000
Estimate quantities to 1000
Count in 3s, 4s, 5s, and explore other numbers
Use number patterns to learn multiplication tables: 1s, 2s, 5s, 10s
Automatically recall basic addition and subtraction facts
Model addition and subtraction equations to 1000 (with and without regrouping)
Use mathematical vocabulary and symbols of multiplication and division:
times, divide, product, factors, x ÷
Use and describe multiple strategies to solve addition, subtraction,
multiplication and division problems
Read, write and model multiplication and division problems
Compare fractions using manipulatives and using fractional notation
Use mathematical vocabulary and symbols of fractions: numerator, denominator,
equivalence
Understand and model the concept of equivalence to 1: two halves = 1,
three thirds = 1
Reasonably estimate answers: rounding and approximation
Select and explain an appropriate method for solving a problem
Analyse patterns in number systems to 100
Recognize, describe and extend more complex patterns in numbers
Understand and use the relationship between addition and subtraction:
4 + 3 = 7, 7 – 3 = 4
Identify patterns and rules for multiplication and division: 4 x 3 =
12, 3 x 4 = 12 and 12 ÷ 3 = 4, 12 ÷ 4 = 3
Model, with manipulatives, the relationship between multiplication and
division model, with manipulatives, the relationship between multiplication
and addition (repeated addition)
Model, with manipulatives, the relationship between division and subtraction
Model multiplication as an array
Understand and use number patterns to solve problems (missing numbers)

Discuss, compare and create sets from data that has subsets using tree, Carroll, Venn and other diagrams
Collect and display data in a bar graph and interpret results
Use the scale on the vertical axis of a bar graph to represent large
quantities
Find, describe and explain the mode in a set of data and its use
Understand the purpose of a database by manipulating the data to answer
questions and solve problems
Use probability to determine mathematically fair and unfair games and
to explain possible outcomes


Estimate, measure, label and compare using formal methods and standard units of measurement: length, mass, time and temperature
Select appropriate tools and units of measurement
Describe measures that fall between numbers on a measure scale: 31/2kg,
between 4cm and 5cm
Estimate, measure, label and compare perimeter and area
Model addition and subtraction using money
Read and write the time to the minute, using intervals of 10 minutes,
5 minutes and 1 minute, on 12-hour analogue and digital clocks

Sort, describe and model regular and irregular polygons: triangles, hexagons, trapeziums
Identify, describe and model congruency in 2-D shapes
Combine and transform 2-D shapes to make another shape
Create symmetrical patterns, including tessellation
Identify lines and axes of reflective and rotational symmetry
Understand an angle as a measure of rotation by comparing and describing
rotations: whole turn; half turn; quarter turn; north, south, east and
west on a compass
Locate features on a grid using coordinates
Number
Pattern and function
Data handling
Shape and Space
The students in
Year 5
will:
Read,
write and model numbers using base ten system up to one million
Count, compare and order numbers up to one million
Estimate quantities beyond a thousand
Automatically recall addition, subtraction, multiplication and division
facts
Create and solve using multiple strategies, addition, subtraction multiplication
and division problems
Use number patterns to solve problems involving larger numbers
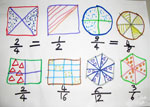
Read, write, model and compare fractions
Understand and model equivalence
Reasonably estimate answers using rounding and approximation
Select, explain and defend various methods for solving problems
Recognise,
describe and extend more complex patterns in numbers
Model and explain number patterns and use patterns to solve problems
Understand and use the relationship among the four operations - addition,
subtraction, multiplication and division
Use real-life problems to create a number pattern following a rule
Design surveys and collect, organise and record data in displays
Create, interpret, discuss and compare data displays
Use a scale on a graph to represent large quantities
Find, describe and explain the mode in a set of data
Discuss, identify, predict and place outcomes in order of likelihood:
impossible, unlikely, likely and certain
Estimate,
measure, label and compare length, mass, time, temperature
Select and use appropriate standard units of measurement
Use measuring tools accurately
Develop procedures for finding perimeter, area and volume
Measure and construct angles in degrees using a protractor
Use and construct time-lines
Read and write the time to the minute and second, using intervals of
10, 5 and 1 minute on twelve and 24-hour clocks
Combine and transform 2-D shapes to make another shape
Create symmetrical patterns, including tessellation
Identify lines and axes of reflective symmetry
Understand that an angle is a measure of rotation
Locate features on a grid using co-ordinates
Use geometric vocabulary of 2-D and 3-D shapes and angles
Classify, sort and label different types of triangles and quadrilaterals
Use a pair of compasses
Number
Pattern and function
Data handling
Shape and Space
The students in
Year 6
will:
Read, write and model numbers to one million and beyond
Automatically use number facts
Read, write, model and compare fractions, decimals and percentages
Interchange fractions, decimals and percentages
Add and subtract decimals to the thousandths
Find and use ratios
Read, write and model additional and subtraction of integers
Use exponential notation
Describe strategies to create and solve more complex problems
Understand and use the relationship between the four operations
Model and explain number patterns and use real-life problems to create
a number pattern following a rule
Develop, explain and model simple algebraic formulas
Model exponents as repeated multiplication
Understand and use exponents and roots as inverse functions
Display and interpret data in a variety of ways, compare data display
Find, describe and explain the range, mode, median and mean in a set
of data
Use a numerical probability scale 0-1 or 1%-100%
Determine theoretical probability of an event and explain why it might
differ from the experimental probability
Estimate, measure, label and compare perimeter, area and volume
Develop procedures for finding perimeter, area and volume
Use the correct tools for any measurement with accuracy
Measure and construct angles in degrees using a protractor
Use and construct 12-hour and 24-hour timetables
Be able to determine time world-wide
Use the mathematical vocabulary of 2-D and 3-D shapes and angles
Classify, sort and label all types of triangles and quadrilaterals
Turn a 2-D net into a 3-D shape and vice versa
Use scale and ratio to enlarge and reduce shapes
Read and plot coordinates in four quadrants
